Causes & Treatment for Uneven Skin Colour
When it comes to skin, many people look towards maintaining an even and glowing complexion. Unfortunately, melasma is a common condition that can cause brown patches across the face and other sun exposed areas. For some people, this can effect their emotional well being and impact their social interaction.
What is melasma?
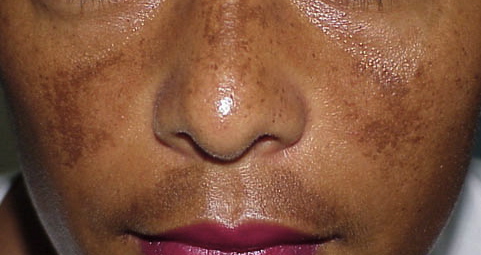
Melasma is a chronic condition. It is a pigmentation disorder causing symmetrical blotchy brown or brown-grey patches on the skin. These patches are most commonly found on the face, particularly the cheeks, bridge of the nose, forehead, upper lip and chin, but other areas that are exposed to sun can also be affected (arms and neck). Some melasma effects pigmentation in the epidermis (the outermost layer of the skin), while other times it effects the dermis deeper down. Some people have a mixed type, affecting both the dermal and epidermal layers. When the deeper dermis is affected, it is more difficult to treat.
Eight triggers and risk factors to developing melasma:
1. Women of reproductive age are more commonly affected than men. Though, 10% of patients seeking treatment for melasma are men. If you have relatives with melasma, there is an increased chance that you may develop it. People with darker skin tones are more affected by melasma.
2. Sun exposure and damage to the skin by sun is the biggest trigger for melasma. The good news is that this is also the most avoidable risk factor.
3. Pregnancy can trigger melasma. In this context, it is known as cholasma (the mask of pregnancy). This is because estrogen and progesterone (hormones involved with reproduction) influence pigment-producing cells in the body. In this situation, the pigmentation often fades a few months after delivery.
4. Just like in pregnancy, hormones taken by a patient can induce melasma. Medications that commonly contain estrogen and progesterone include the oral contraceptive pill, hormone replacement therapy, and interuterine devices.
5. Certain non-hormone based medications may trigger melasma. These include some new cancer therapies and anti-epileptic medications.
6. Cosmetics can trigger melasma, so people need to be careful. Certain soaps, deodorant soaps and cosmetics can cause a phototoxic reaction that triggers melasma.
7. Thyroid disorders may trigger melasma.
8. For some individuals facial waxing can cause skin inflammation, which can trigger melasma.
Two treatments for melasma:
1. Prevent Pigment Gain
The most important thing that can be done to prevent and help melasma is sun protection. Wear sunscreen everyday containing at least SPF 30. Reapply every 2 hours when out in the sun. It’s a good idea to wear make up that contains sunscreen. Mineral makeup is a great option. It provides excellent camouflage to existing melasma, and because it contains titanium dioxide and zinc oxide, it provides additional sun protection.
2. Promote Pigment Loss
- Topical Therapies:
- Preparations that inhibit melanin productions (the cells that produce skin pigment) or skin lightening agents. Some of these products can be found at the drug store, but physicians can prescribe these in higher more effective concentrations if the over the counter preparations are not providing benefit. It is important to be monitored by a physician as some of these products can cause an irritation to the skin. In patients with sensitive skin, this could cause new post-inflammatory pigmentation problems.
- hydroquinone
- azelic acid (safe for use in pregnancy)
- Kojic acid
- Vitamin C
- Preparations that inhibit melanin productions (the cells that produce skin pigment) or skin lightening agents. Some of these products can be found at the drug store, but physicians can prescribe these in higher more effective concentrations if the over the counter preparations are not providing benefit. It is important to be monitored by a physician as some of these products can cause an irritation to the skin. In patients with sensitive skin, this could cause new post-inflammatory pigmentation problems.
- Other topical therapies
- Topical corticosteroids
- Soybean extracts
- Agents that induce peeling of the epidermis. These agents are more effective when the melasma is more superficial in the epidermis.
- Topical retinoids such as tretinoin (do not use in pregnancy)
- Topical alpha hydroxyl acid
The most successful topical method is using these therapies in combinations under the guidance of a physician. Many people will experience improvement using a cream that combines hydroquinone, tretinoin and moderate potency topical steroids.
- Physical Methods
- Chemical Peels
- Microdermabrasion
- Laser and light therapies under the care of a skin specialist
In summary, there are many options to treat uneven skin tone. Please consult a skin professional whom you trust.
